32
VARIABLE MOTION.
[Book I.
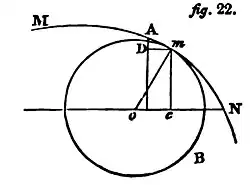
83. The circle  , fig. 22, which coincides with a curve or curved surface through an indefinitely small space on each side of
, fig. 22, which coincides with a curve or curved surface through an indefinitely small space on each side of  the point of contact, is called the curve of equal curvature, or the oscillating circle of the curve
the point of contact, is called the curve of equal curvature, or the oscillating circle of the curve  , and
, and  is the radius of curvature.
is the radius of curvature.
 In a plane curve the radius of curvature
In a plane curve the radius of curvature  , is expressed by
, is expressed by

and in a curve of double curvature it is
 ,
,
 being the constant element of the curve.
being the constant element of the curve.
Let the angle  be represented by
be represented by  , then if
, then if  be the indefinitely small but constant element of the curve
be the indefinitely small but constant element of the curve  , the triangles
, the triangles  and
and  are similar; hence
are similar; hence  or
or  , and
, and  . In the same manner
. In the same manner  ,
,
But  , and
, and  ; also
; also  , and
, and  ; but these evidently become
; but these evidently become
 and
and  ; or
; or
 and
and 
Now if  the radius of curvature be represented by
the radius of curvature be represented by  , then
, then  being the indefinitely small increment
being the indefinitely small increment  of the angle
of the angle  , we have
, we have  ; for the sine of the infinitely small angle is to be
considered as coinciding with the arc: hence
; for the sine of the infinitely small angle is to be
considered as coinciding with the arc: hence  , whence
, whence  . But
. But  , and as
, and as  is constant
is constant  . Whence
. Whence  , or
, or  ,
,
 In a plane curve the radius of curvature , is expressed by
In a plane curve the radius of curvature , is expressed by